# 一. 背景
- Module Federation
[ˌfedəˈreɪʃn]使 JavaScript 应用得以在客户端或服务器上动态运行另一个 bundle 的代码。
Multiple separate builds should form a single application. These separate builds should not have dependencies between each other, so they can be developed and deployed individually.
This is often known as Micro-Frontends, but is not limited to that.
1
2
3
2
3
- 翻译过来:
多个独立的构建可以形成一个应用程序。这些独立的构建不会相互依赖,因此可以单独开发和部署它们。
这通常被称为微前端,但并不仅限于此。
1
2
2
# 二. 价值
- 场景
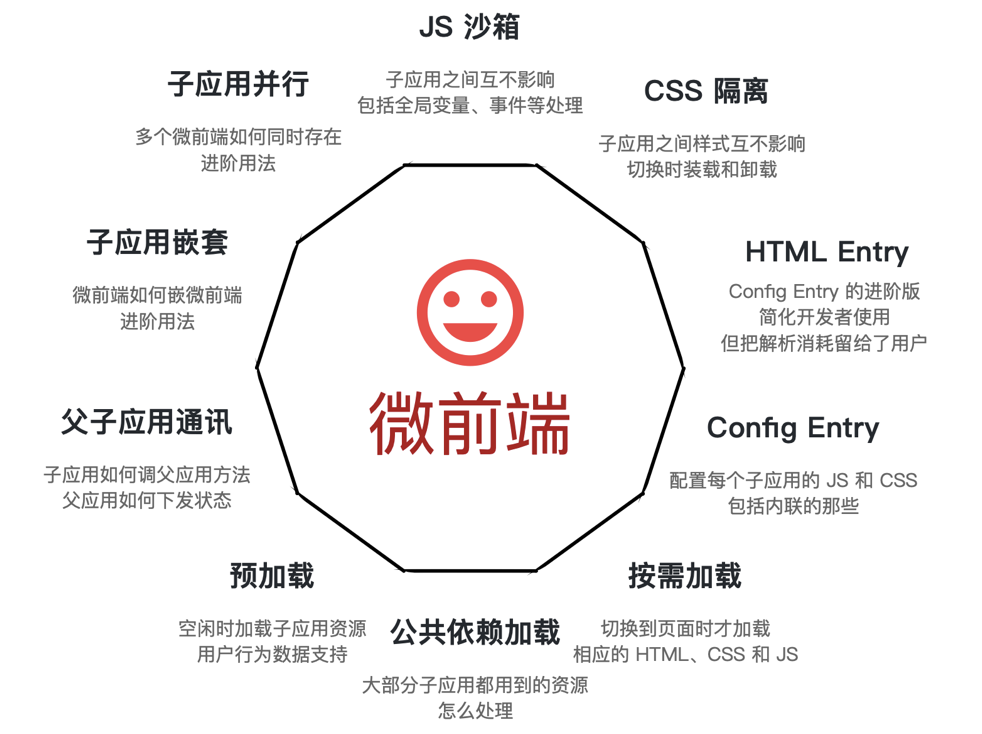
# 三. 实践
...
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require("html-webpack-plugin");
const ModuleFederationPlugin = require("webpack/lib/container/ModuleFederationPlugin");
module.exports = {
// 其他webpack配置...
plugins: [
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: 'empBase',
library: { type: 'var', name: 'empBase' },
filename: 'emp.js',
remotes: {
app_two: "app_two_remote",
app_three: "app_three_remote"
},
exposes: {
'./Component1': 'src/components/Component1',
'./Component2': 'src/components/Component2',
},
shared: ["react", "react-dom","react-router-dom"]
})
]
}
...
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
- 初步认识需要配置的属性:
| 字段名 | 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| name | string | 必传值,即输出的模块名,被远程引用时路径为${name}/${expose} |
| library | object | 声明全局变量的方式,name为umd的name |
| filename | string | 构建输出的文件名 |
| remotes | object | 远程引用的应用名及其别名的映射,使用时以key值作为name |
| exposes | object | 被远程引用时可暴露的资源路径及其别名 |
| shared | object | 与其他应用之间可以共享的第三方依赖,使你的代码中不用重复加载同一份依赖 |
# 四. 构建过程
- 让我们看看构建后的代码:
var moduleMap = {
"./components/Comonpnent1": function() {
return Promise.all([__webpack_require__.e("webpack_sharing_consume_default_react_react"), __webpack_require__.e("src_components_Close_index_tsx")]).then(function() { return function() { return (__webpack_require__(16499)); }; });
},
};
var get = function(module, getScope) {
__webpack_require__.R = getScope;
getScope = (
__webpack_require__.o(moduleMap, module)
? moduleMap[module]()
: Promise.resolve().then(function() {
throw new Error('Module "' + module + '" does not exist in container.');
})
);
__webpack_require__.R = undefined;
return getScope;
};
var init = function(shareScope, initScope) {
if (!__webpack_require__.S) return;
var oldScope = __webpack_require__.S["default"];
var name = "default"
if(oldScope && oldScope !== shareScope) throw new Error("Container initialization failed as it has already been initialized with a different share scope");
__webpack_require__.S[name] = shareScope;
return __webpack_require__.I(name, initScope);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
可以看到,代码中包括三个部分:
- moduleMap:通过exposes生成的模块集合
- get: host通过该函数,可以拿到remote中的组件
- init:host通过该函数将依赖注入remote中
再看moduleMap,返回对应组件前,先通过__webpack_require__.e加载了其对应的依赖,让我们看看__webpack_require__.e做了什么:
__webpack_require__.f = {};
// This file contains only the entry chunk.
// The chunk loading function for additional chunks
__webpack_require__.e = function(chunkId) {
// 获取__webpack_require__.f中的依赖
return Promise.all(Object.keys(__webpack_require__.f).reduce(function(promises, key) {
__webpack_require__.f[key](chunkId, promises);
return promises;
}, []));
};
__webpack_require__.f.consumes = function(chunkId, promises) {
// 检查当前需要加载的chunk是否是在配置项中被声明为shared共享资源,如果在__webpack_require__.O上能找到对应资源,则直接使用,不再去请求资源
if(__webpack_require__.o(chunkMapping, chunkId)) {
chunkMapping[chunkId].forEach(function(id) {
if(__webpack_require__.o(installedModules, id)) return promises.push(installedModules[id]);
var onFactory = function(factory) {
installedModules[id] = 0;
__webpack_modules__[id] = function(module) {
delete __webpack_module_cache__[id];
module.exports = factory();
}
};
try {
var promise = moduleToHandlerMapping[id]();
if(promise.then) {
promises.push(installedModules[id] = promise.then(onFactory).catch(onError));
} else onFactory(promise);
} catch(e) { onError(e); }
});
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
通读核心代码之后,可以得到如下总结:
- 首先,mf会让webpack以
filename作为文件名生成文件 - 其次,文件中以var的形式暴露了一个名为
name的全局变量,其中包含了exposes以及shared中配置的内容 - 最后,作为
host时,先通过remote的init方法将自身shared写入remote中,再通过get获取remote中expose的组件,而作为remote时,判断host中是否有可用的共享依赖,若有,则加载host的这部分依赖,若无,则加载自身依赖。
